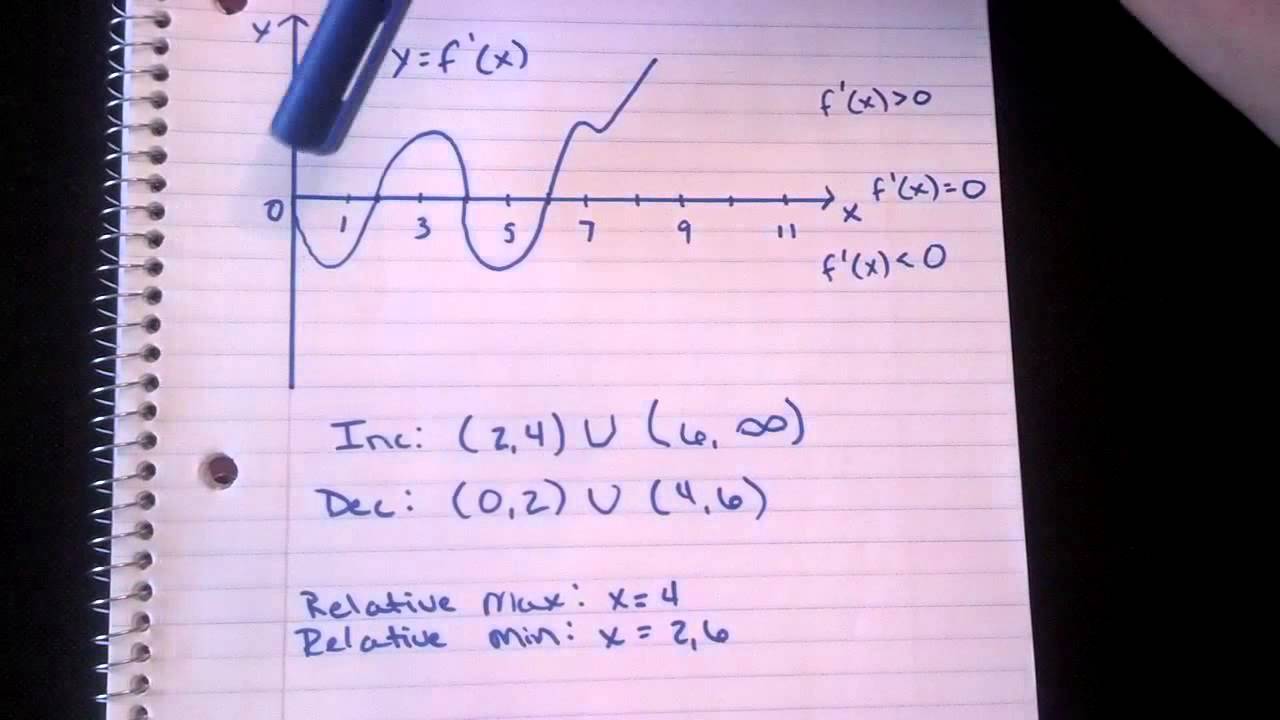
Find the relative/local maxima/minima of theIf f′(x) > 0 on an interval, then f is INCREASING on that interval If f′(x) < 0 on an interval, then f is DECREASING on that interval A function has a LOCAL MAXIMUM at x = a if f(a) ≥ f(x) for all x "near" aSolution for On what interval(s) is f(x) decreasing, if any?
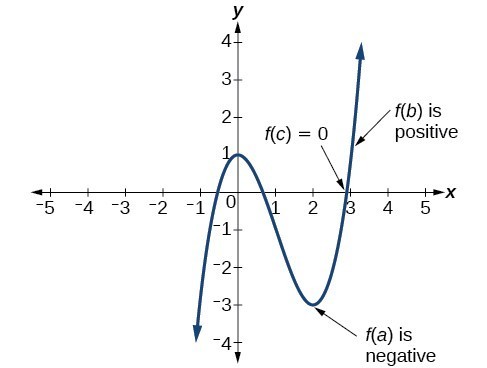
Use The Intermediate Value Theorem College Algebra
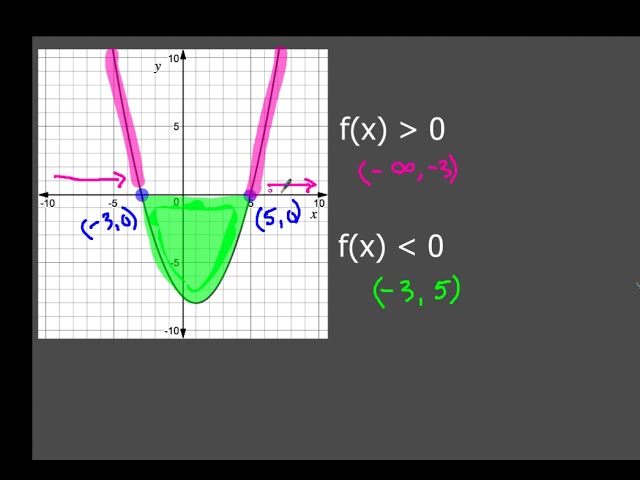
F(x) 0 over the intervals (–∞ –3) and brainly
F(x) 0 over the intervals (–∞ –3) and brainly-First, take the derivative Set equal to 0 and solve Now test values on all sides of these to find when the function is positive, and therefore increasing I will test the values of 0, 2, and 10 Since the value that is positive is when x=0 and 10, the interval is increasing in both of those intervalsFirst find the critical point where f'(x) = 0 If a function continuous on interval a, b and differentiable in (a, b) If f'(x) > 0 for all x in (a, b), then f is increasing on a, b If f'(x) < 0 for all x in (a, b), then f is decreasing on a, b If f'(x) = 0 for all x in (a, b), then f is constant on a, b Calculation Given
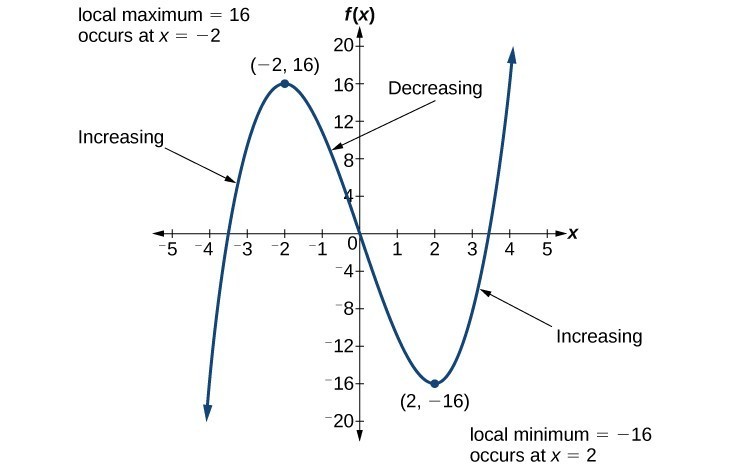



Use A Graph To Determine Where A Function Is Increasing Decreasing Or Constant College Algebra
Momentarily, we will discuss the meaning of Riemann sums in the setting when f is sometimes negative The second column is labeled f of x with entries 8, 4, 0, negative 2, negative 2, 0, 4 Which is a valid calculus consider the equation below f(x)=e^(7x)e^(x) find the intervals on which f is increasing and decreasing (enter your answers using interval notation) find the local minimum of f find the interval on which f is concave upFind the Intervals in Which F(X) = Sin X − Cos X, Where 0 < X < 2π is Increasing Or Decreasing ?
Find the absolute extremums on the given interval {eq}f(x)=\frac{x}{x^2x1},(0,3) {/eq} Absolute Extreme for Functions The functions have extreme values in a study interval It is common toAnswer to Assume f(x) is continuous on an interval around x=0, except possibly at x=0 What does the table of values suggest as the integer value for Teachers for Schools for Working ScholarsSo f is concave down on these intervals, and f00(x) > 0 on the interval x = (π/6,5π/6) so f is concave up on this interval Thus, we see that f switches concavity at the points x = π/6,5π/6 ie, so these are the inflection points of f 7 Exercise 43 Find
Advertisement Remove all ads For our second interval (1,1), let the test value be x=0 `f'(0)=(10^2)/(0^21)^2=1` (Increasing) And for our third interval, let the test value be x=2Determine the open intervals on which f(x)=3x^44x^312x^25 is increasing or decreasing Determine the open intervals on which f(x)=3x^44x^312x^25 is increasing or decreasing



Http Mysite Science Uottawa Ca Phofstra Mat1300 Lecture09 Pdf
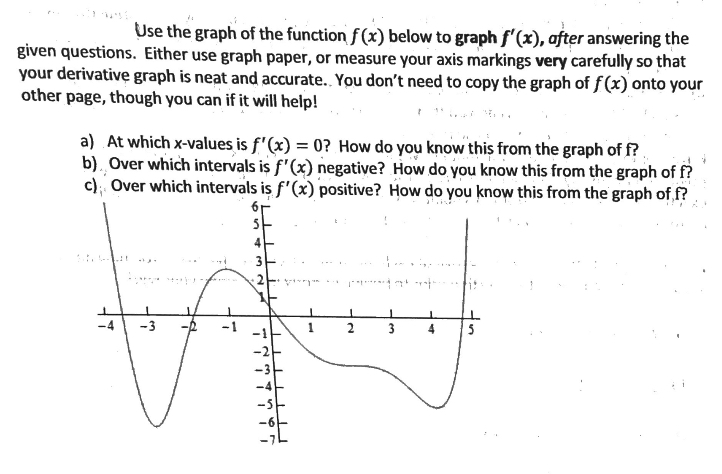



Prod Qna Question Images S3 Amazonaws Com Qna I
F ′ (x) = 0 when the numerator of f ′ (x) is 0 That occurs when x 22 x3 = (x3) (x 1) = 0;Algebra Convert to Interval Notation x>=0 x ≥ 0 x ≥ 0 Convert the inequality to interval notation 0,∞) 0, ∞)B) If f'(x) 0 on an interval, then f is concave upward on that interval d) If f''(x)



1
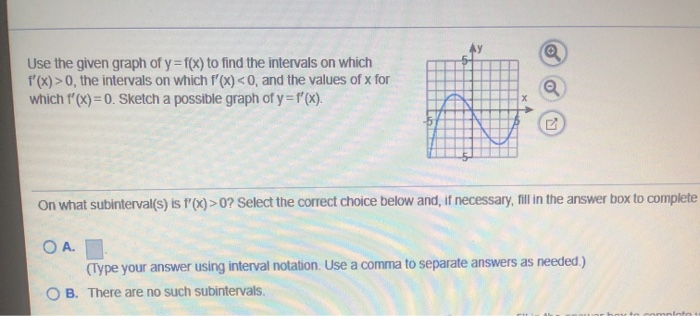



Use The Given Graph Of Y F X To Find The Intervals Chegg Com
If f′(x) > 0, then f is increasing on the interval, and if f′(x) < 0, then f is decreasing on the interval This and other information may be used to show a reasonably accurate sketch of the graph of the function Example 1 For f(x) = x 4 − 8 x 2 determine all intervals where f(2xx )2 >0 ,equality occurs when x = 0 and from domain (1x)> 0 which also means 1x1 > 0 so from this we can say that f ′(x) > 0 for all x > −1 ,except for x = 0 it becomes 0 so therefore we conclude that f (x) increases in the intervals xϵ(−1,0) and xϵ(0,∞)I would like to answer this more intuitively (less rigorously) The derivative of a function f(x) is basically the rate of change of f(x) with respect to x Thus if the derivative is negative, it implies that f(x) is not only changing with respect




Ex 6 2 4 Find Intervals F X 2x2 3x Is A Increasing




Example 12 Find Intervals Where F X Sin 3x Is Decreasing
If f′′(x) < 0 for all x ∈(a,b), then f is concave down on (a,b) Defn The point (x 0 ,y 0 ) is an inflection point if f is continuous at x 0 and if the concavity changes at x 0X 2 = 75 3 x 2 = 75 3 Divide 75 75 by 3 3 x 2 = 25 x 2 = 25 x 2 = 25 x 2 = 25 Take the square root of both sides of the equation to eliminate the exponent on the left side x = ± √ 25 x = ± 25 The complete solution is the result of both the positive and negative portions of the solutionIf $f '(x) > 0$ on an open interval, then $f$ is increasing on the interval If $f '(x) < 0$ on an open interval, then $f$ is decreasing on the interval DO Ponder the graphs in the box above until you are confident of why the two conditions listed are true




F X Lt 0 Over 3 And What Other Interval O 2 4 1 1 O 3 1 1 O 1 1 2 O 1 1 Brainly Com



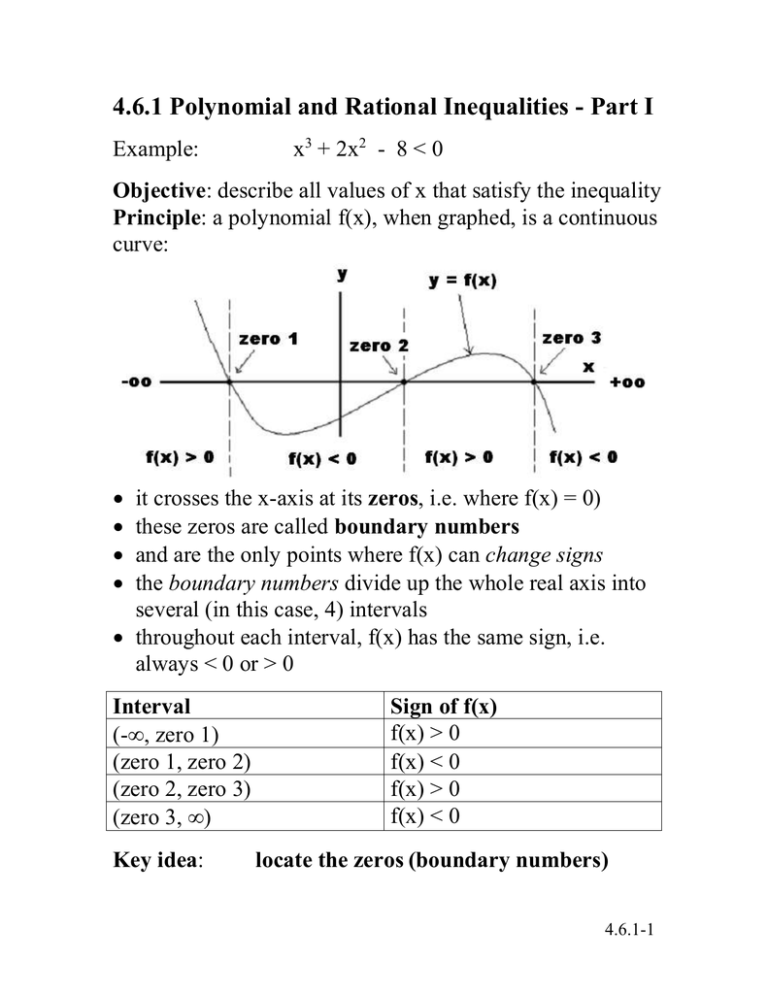
Solving Polynomial Inequalities By Graphing
Which statement is correct?Math 151 cBenjamin Aurispa 51DerivativesandGraphs What does f′ say about f?Section 51 The First Derivative Increasing/Decreasing Test (a) If f0(x) > 0onaninterval,thenf is increasing on that interval (b) If f0(x) < 0onaninterval,thenf is decreasing on that interval Definition A critical number of a function f is a number c in the domain of f such that either f0(c)=0orf0(c)doesnotexist 1 Find the critical numbers for f(x)=x2 6x




Use The Given Graph Of F X To Determine The Intervals Where F X Greater Than 0 F X Less Than 0 The X Values Where F X 0 And Where F X Is




Positive Negative Intervals Of Polynomials Article Khan Academy
If a, b ∈ R and a < b, the following is a representation of the open and closed intervals Open interval is indicated by (a, b) = {x a < y < b} Closed interval is indicated by a, b = {x a ≤ x ≤ b} The mandatory condition for continuity of the function f at point x = a considering a to be finite is that lim x→a– f (x) and lim We use the second derivative test and find that f is concave down on (oo ;Indeed, let f(x) be a differentiable function on an interval I, with f '(x) =0, for every Then for any a and b in I, the Mean Value Theorem implies for some c between a and b So our assumption implies Thus f(b) = f(a) for any aand b in I, which means that f(x) is constant




Finding Decreasing Interval Given The Function Video Khan Academy
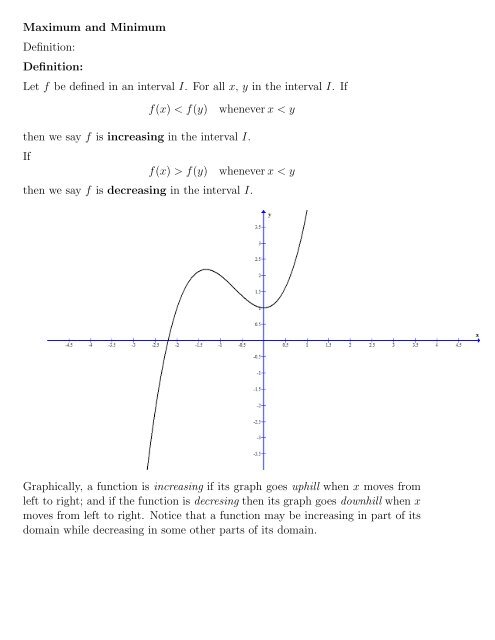



Let F Be Defined In An Interval I For All X Y In The Interval I
Answer On the interval 0,3 the function f( x)= °2 p 2 9 has a global maximum of °3 p at x= p and a global minimum of 6 at x=0 Although a it is not a necessary part of the solution of this exercise, it is instructive to look at a graph of f( x) = °2 p 2 9 on the interval 0,3 Note that the global maximum happens at the critical point Transcript Example 12 Find intervals in which the function given by f (x) = sin 3x, x, ∈ 0, 𝜋/2 is (a) increasing (b) decreasing f(𝑥) = sin 3𝑥 where 𝑥 ∈ 0 ,𝜋/2 Finding f'(x) f'(𝑥) = 𝑑(sin3𝑥 )/𝑑𝑥 f'(𝑥) = cos 3𝑥 × 3 f'(𝒙) = 3 cos 3𝒙 Putting f'(𝒙) = 0 3 cos 3𝑥 = 0 cos 3𝑥 = 0 We know that cos θ = 0If f(x) > 0, then the function is increasing in that particular interval If f(x) < 0, then the function is decreasing in that particular interval Example 1 Find the intervals in which f(x) = 2x³x²x is increasing or decreasing Solution f(x) = 2x 3 x 2 x Step 1 f'(x) = 6x² 2x ÷ by 2 ⇒ 3x²x10 Step 2 f'(x) = 0
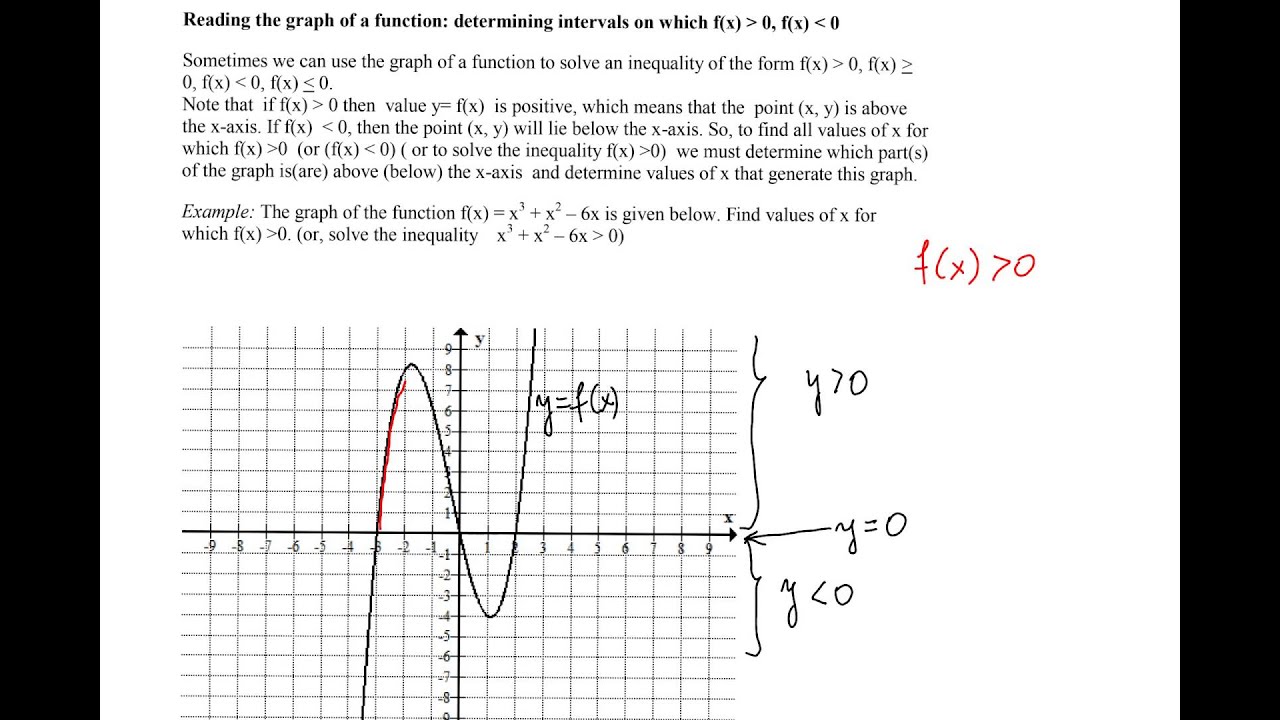



Reading The Graph Of A Function Intervals On Which Fx Is Positive Negative Youtube



The Graph Of Y F X Is Shown To The Right Identify Chegg Com
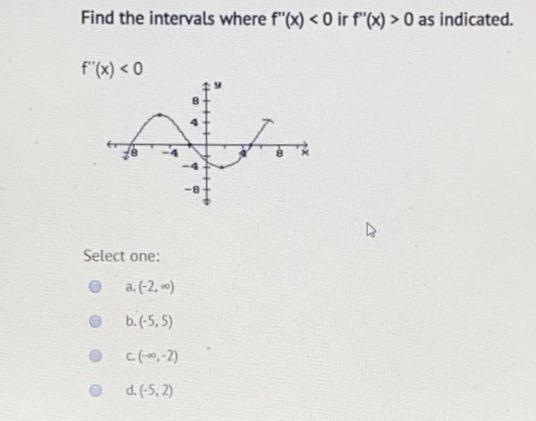
Solution for Find the intervals where f"(x) < 0 or f"(x) > 0 as indicated f"(x) < 0 (1, 0) O (1, 0) (00, 1) (1, 0), (1, o0) Answered Find the intervals where f"(x) < 0 or bartleby menu If f(x) = x/2 1, then on the interval 0, pi (a) tan f (x) and 1/f(x) are both continuous (b) tan f (x) and 1/f(x) are both discontinuous (c) tan f (x) and f1 (x) are both continuous (d) tan f (x) is continuous but 1/f(x) is not continuous0 If c is the midpoint of the interval a, b and f(c) <




Use The Intermediate Value Theorem College Algebra




Use A Graph To Determine Where A Function Is Increasing Decreasing Or Constant College Algebra
On the interval (1, 3), the function f(x) = 3x 2/x is (A) Strictly decreasing (B) Strictly increasing asked in Limit, continuity and differentiability by Rozy (Sqrt2)uu(0;sqrt2) and concave up on (sqrt2;0)uu(sqrt2;oo) For concavity we use the second derivative test f'(x)=15x^460x^2 f''(x)=60x^31x =60x(x^22) This second derivative equals zero if x = 0 or x = sqrt2 or x = sqrt2Rolle's Theorem – Let f be continuous on the closed interval a, b and differentiable on the open interval (a, b) If f a f b '0 then there is at least one number c in (a, b) such that fc Examples Find the two xintercepts of the function f and show that f'(x) = 0 at some point between the two xintercepts 1 f x x x 3 2 f x x x31



Below Is The Graph Of The Function F X Determine Chegg Com




The Graph Of The Derivative F X Of A Function F Is Shown Below On What Intervals Is F Increasing Why On What Intervals Is F Decreasing Why If It Is Known That
We know that any squared expression is greater than or equal to zero; The derivative of the function $f$ that is defined in the open interval is $$\frac{df}{dx}(0,1) \to \mathbb{R}$$ $$\frac{df}{dx}(x)=\lim_{h\to 0} \frac{f(xh)f(x)}{h}= \lim_{h\to 0} \frac{xhx}{h}= \lim_{h\to 0} \frac{h}{h} = \lim_{h\to 0} 1=1$$Consider the function f defined on the interval (5,5) as follows, 0, x 65, 0), f (x) = x, x € 10,5) Denote by ff the Fourier series expansion of f on (5,5), NXX $# (x) = m 3 o, cos ("EY) b, sin (NE) Find the coefficients ao a,, and by, with n > 1 M ao = a, мм be II Let u be the solution to the initial boundary value problem for




A Determine The Intervals On Which X 0 And The Intervals On Which 34 X O Display Your Answer In The Form Of A Sign Chart For F 34 H Using Your Answer
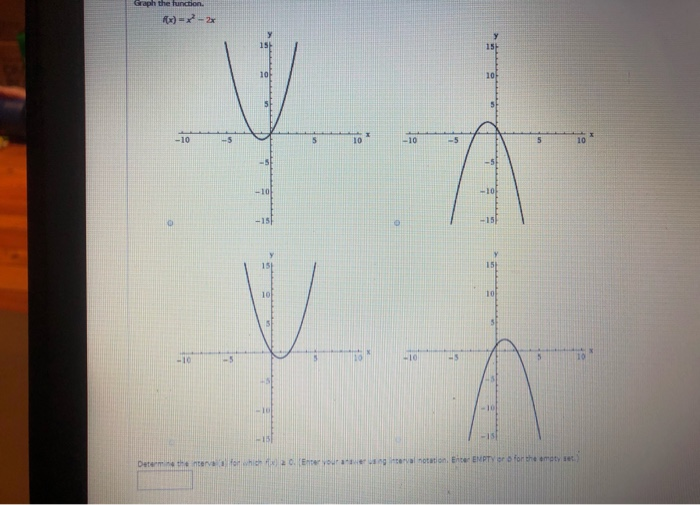



Determine The Interval S For Which F X 0 Enter Chegg Com
Consider the given function and the given interval f(x) = 10 sin(x) − 5 sin(2x), 0, π (a) Find the average value fave of f on the given interval (b) Find c such that fave = f(c) (Round your answers to three decimal calculus 1 Find the average value have of the function h on the given interval h(x) = 2 cos4(x) sin(x), 0, π 2 Consider the given function and the given interval f(x) = 6 sin(x) − 3 sin(2x), 0 When f (x) ≥ 0 on a, b, each of the Riemann sums Ln, Rn, and Mn provides an estimate of the area under the curve y = f (x) over the interval a, b;Example 14 Define f 0,1 → Rby f(x) = (1/x if 0 < x ≤ 1, 0 if x = 0 Then Z 1 0 1 x dx isn't defined as a Riemann integral becuase f is unbounded In fact, if 0 < x1 < x2 < ··< xn−1 < 1 is a partition of 0,1, then sup 0,x1 f = ∞, so the upper Riemann sums of f are not welldefined An integral with an unbounded
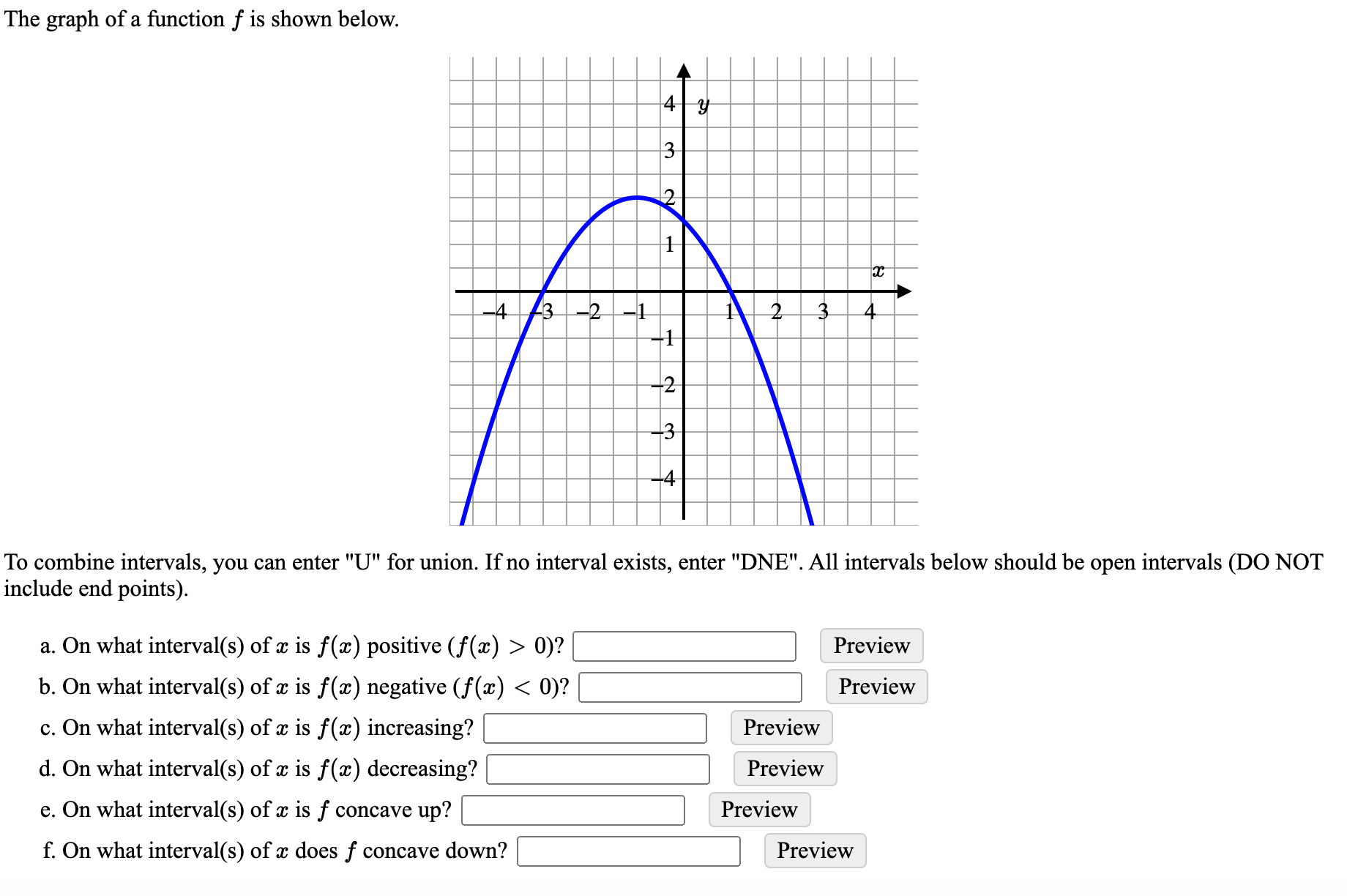



Answered The Graph Of A Function F Is Shown Bartleby
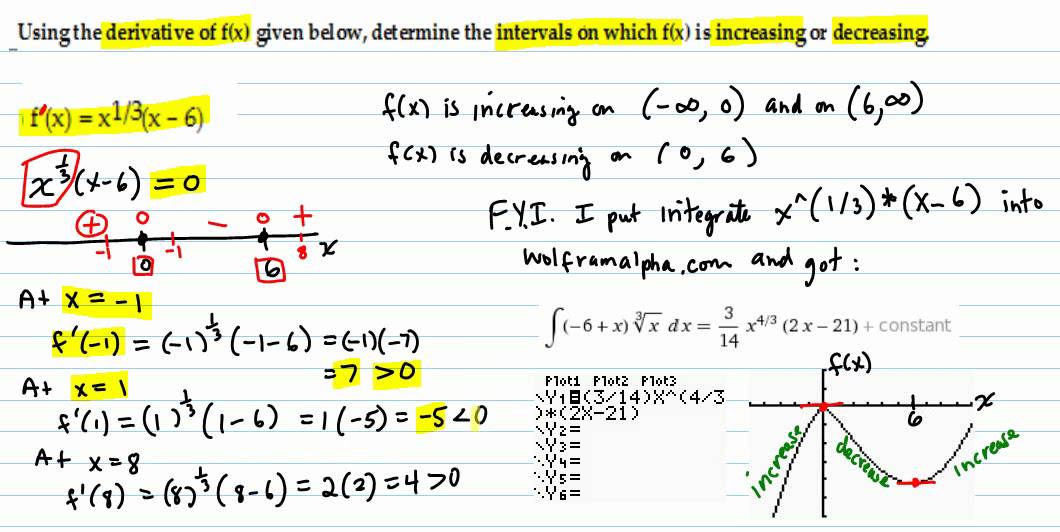



Use F X To Determine Intervals Where F X Is Increasing Or Decreasing Youtube
Both factors are negative, so is positive (You can also get this by just evaluating ) On the interval , pick One factor () is positive, while the other () is negative, so the product is negative Or just evaluate On the interval , pick Both factors are positive, so is positive Note that all we need here is the sign of , not its valueOn what interval(s) is f(x) increasing, if any?A General Note Local Minima and Local Maxima A function latexf/latex is an increasing function on an open interval if latexf\left(b\right)>f\left(a\right)/latex for any two input values latexa/latex and latexb/latex in the given interval where latexb>a/latex A function latexf/latex is a decreasing function on an open interval if latexf\left(b\right)




Oneclass 1 Point Letf X 2yx 6x For X Gt 0 Find The Open Intervals On Which Is Increasing
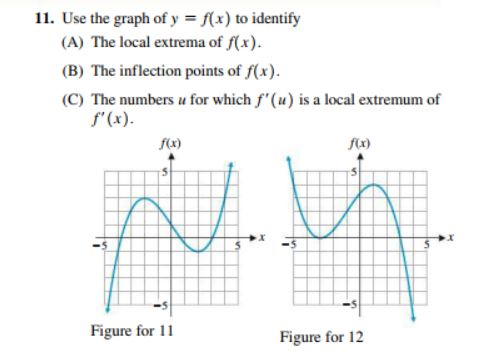



A 9 Use The Graph Of Y F X Assuming F X 0 If Chegg Com
3 Consider the equation below F(x) = 5 sin x 5 cos x, 0A function f (x) is continuous over some closed interval a,b if for any number x from the OPEN interval (a,b) there exists twosided limit which is equal to f (x) and a righthand limit for a_ from a,b and lefthand limit for _b from a,b, where they are equal to f (a) and f (b) respectively So in order a function f (x) to be continuousIntegration are from x 0 to x 2p Thus if f is defined on the interval (0,L), we identify 2 p L or p L 2 The resulting Fourier series will give the periodic extension of f with period L In this manner the values to which the series converges will be the same on (Identity reflection L, 0) as on (0, L) _L L x y x y L _L L f(x) = f(x L) x
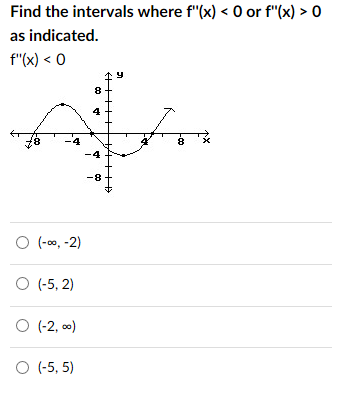



Find The Intervals Where F X 0 Or F X 0 As Chegg Com




Solved Which Statement Is True About The Graphed Function F X F X Lt 0 Over The Intervals Brainly Com
Ex 62, 3 Find the intervals in which the function f given by f (𝑥) = sin 𝑥 is (a) strictly increasing in (0 , 𝜋/2) f(𝑥) = sin 𝑥 f'(𝒙) = cos 𝒙Since cos 𝑥 > 0 for 𝑥 ∈ ("0 , " 𝜋/2)∴ f'(𝑥) < 0 for 𝑥 ∈ (0 , π) Thus, f is strictly increasing in ("0 , " 𝜋/2)Roughcos 0 = 1 cos 𝜋/4 = 1/√2cos 𝜋/2 = 0Value of cos𝑥 > 0 for (0 , 𝜋/2)Ex 62, 3 Find the intervals in which the function f given by f (𝑥) = Sin x is (b) strictly 0 Notice that the graph of f crosses the x axis at − 3, − 2, 0, 2 and 3 Using the fact f ( x) > 0 on the interval where the graph is above the x axis, and f ( x) < 0 on the interval where the graph is below the x axis we have a f ( x) > 0 for x ∈ ( − 3, − 2) ∪ ( 0, 2) ∪ ( 3, ∞)0 and f(b) >
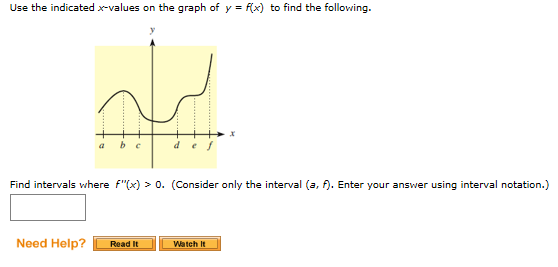



Use The Indicated X Values On The Graph Of Y X To Chegg Com



2
f ''(x) = − cos(x) And since we need to refer to the 0,2π interval, the cosine is positive in 0, π 2, negative in π 2, 3π 2, and again positive in 3π 2,2π The second derivative is −cos(x), so it will change negative areas with positive ones, but the switch points will still be π 2 and 3π 2 Answer linkIe, when x =1, 3When finding the root of f(x)=0 on the interval a, b using the bisection method we know that f(a) <
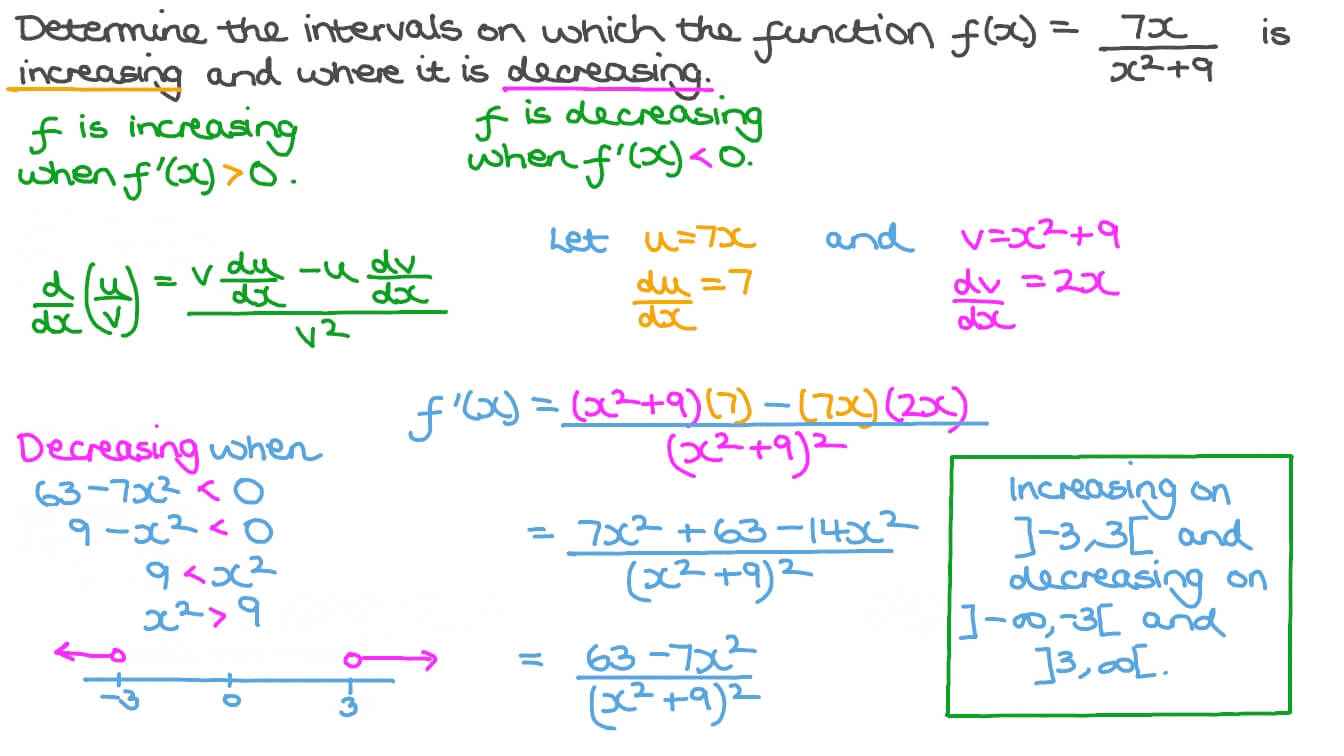



Question Video Finding The Intervals Of Increasing And Decreasing Of A Rational Function Nagwa



Solution If F X X X 1 X 4 Use Interval Notation To Give All Values Of X Where F X Gt 0
Morevoer, since f'(x)0 in (infinity, 1) u (3,5), we see that f is decreasing in (infinity, 1) u (3,5) Example 2 Suppose f'(x) = (x1)(x3)(x7) , then f'(x)>0 in (infinity, 1) u (3,7) and hence f is increasing in those intervals On the other hand, f'(x)0 in (1,3) union (7, infinity), so f0 then the next step in the bisection method would be?CBSE CBSE (Science) Class 12 Question Papers 1851 Textbook Solutions Find the intervals in which f(x) = sin x − cos x, where 0 < x < 2π is increasing or decreasing ?




Use The Given Graph Of F X To Determine The Intervals Where F X 0 F X 0 And The X Values Where F X 0 And Where F X Is Undefined Then Sketch A Graph



Http Www Mast Queensu Ca Math121 Assignments Unit06 Pdf
A The product f(c)*f(b) is positive, so we put a = c and go to the next iteration
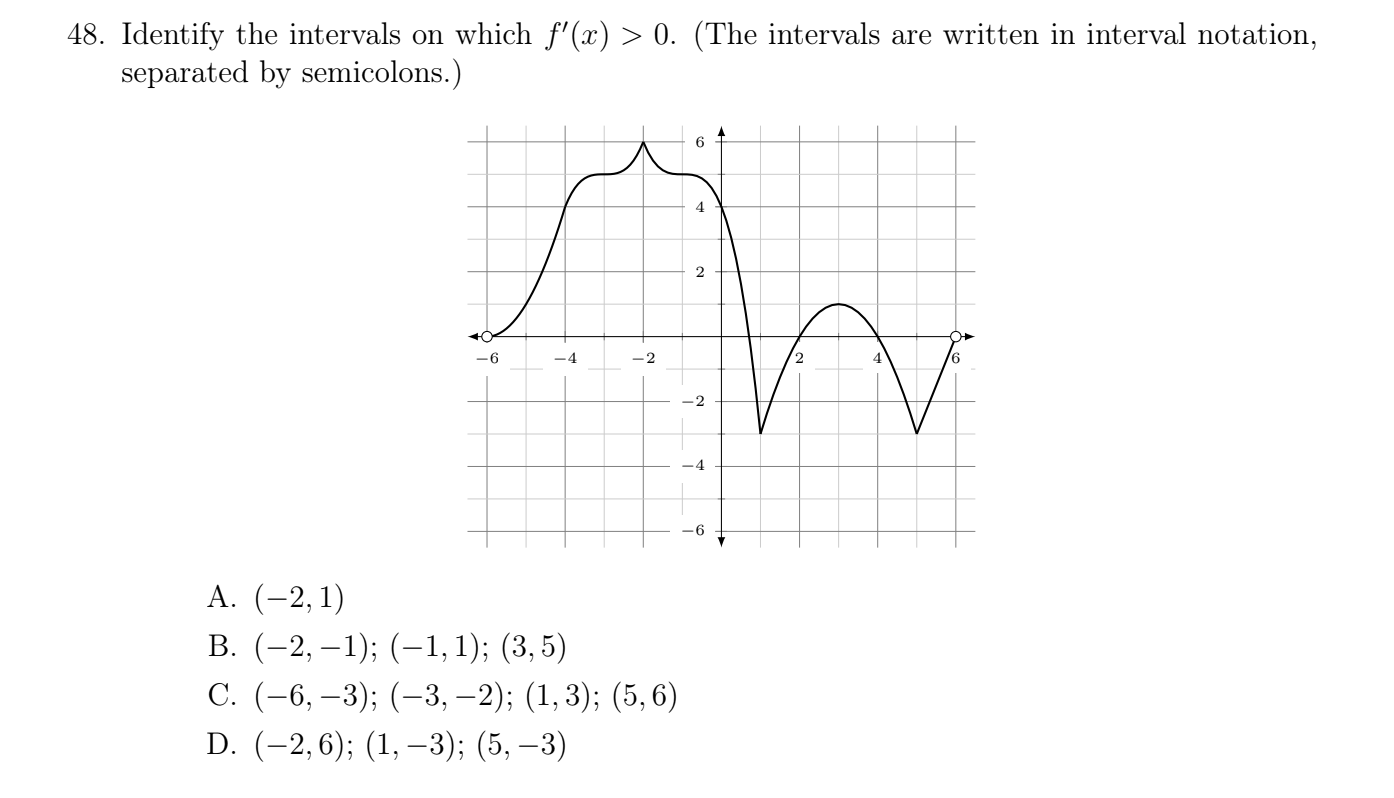



48 Identify The Intervals On Which F X 0 The Chegg Com




4 3 How Derivatives Affect The Shape Of A Graph Facts If F X 0 On An Interval A B Then F X Is Increasing On A B If F X 0 On Ppt Download
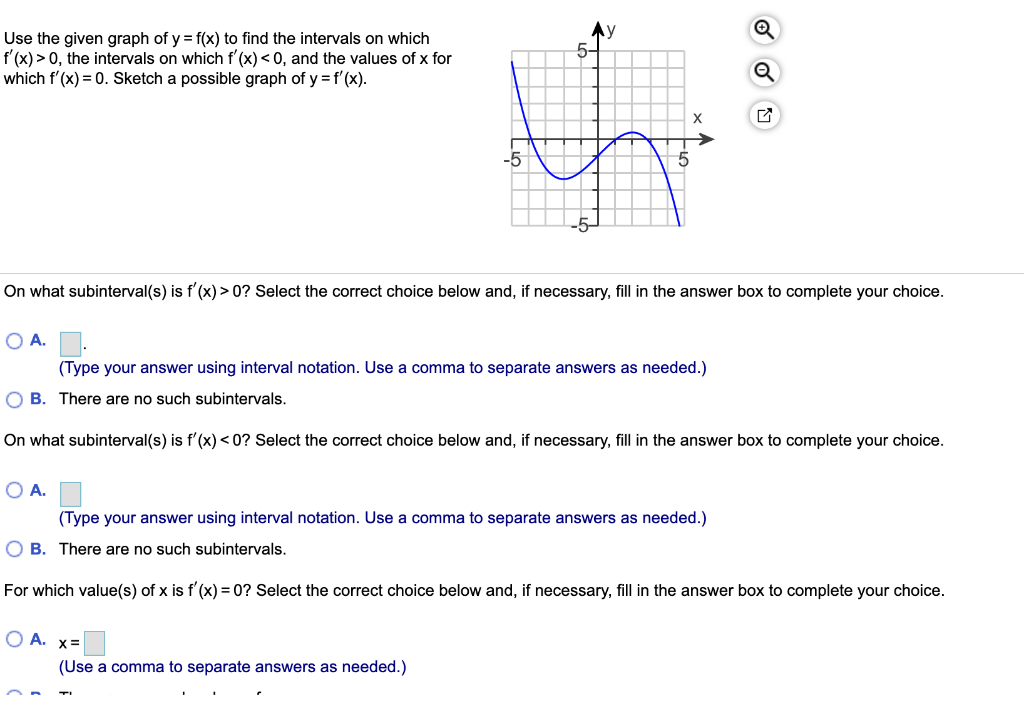



5 Use The Given Graph Of Y F X To Find The Chegg Com



Sage Calculus Tutorial Continuity




If F X 0 On An Interval Then F Is Concave Up On Chegg Com



Web Viu Ca Pughg Summer12 Math121m12n01 Secondderivativenotes Pdf



If F X X 4 8x 2 16 Then For Which Intervals Is F X Increasing Quora
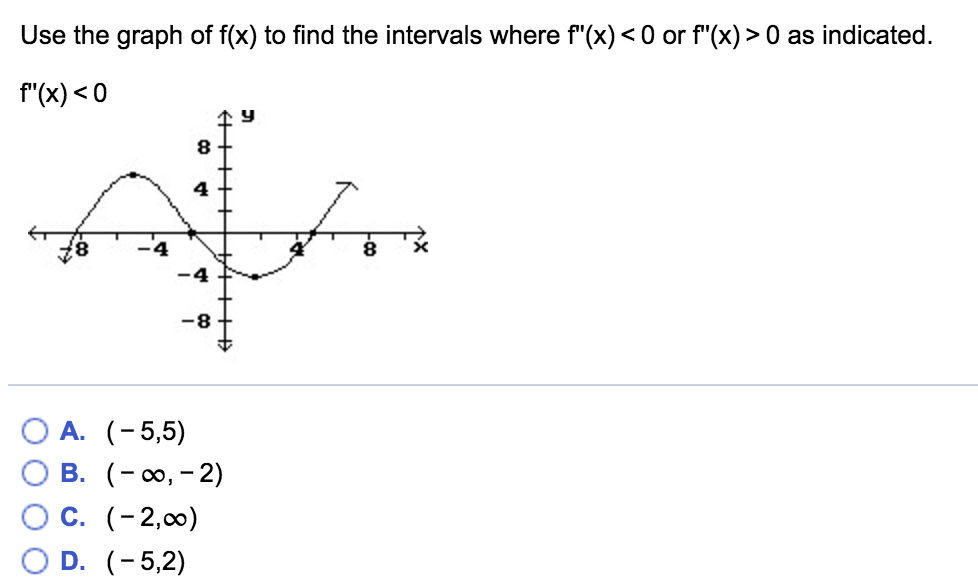



Use The Graph Of F X To Find The Intervals Where Chegg Com
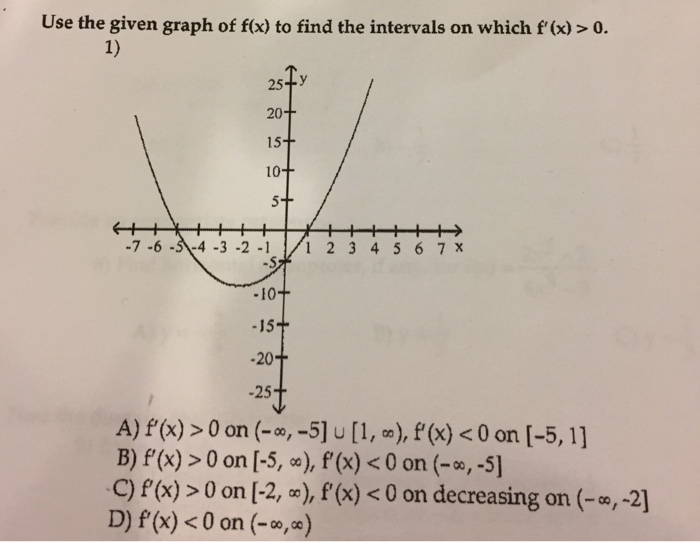



Use The Given Graph Of F X To Find The Intervals On Chegg Com




Answered Use The Given Graph Of F X To Find The Bartleby
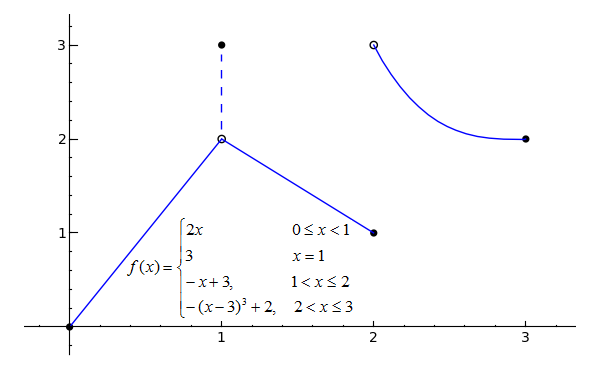



Sage Calculus Tutorial Continuity




Answered Use The Graph Of F To Determine Each Of Bartleby




Example 10 Find The Intervals In Which F X X2 4x 6



Calc 1000 Intervals Of Increase And Decrease



How To Use The Graph Of F To Identify The Intervals On Which F Is Increasing Or Decreasing Youtube



2 1 First Derivative Info




Intervals For X 0 I By Cone N 2 000 A 05 Download Table



Increasing And Decreasing Functions



F X 0
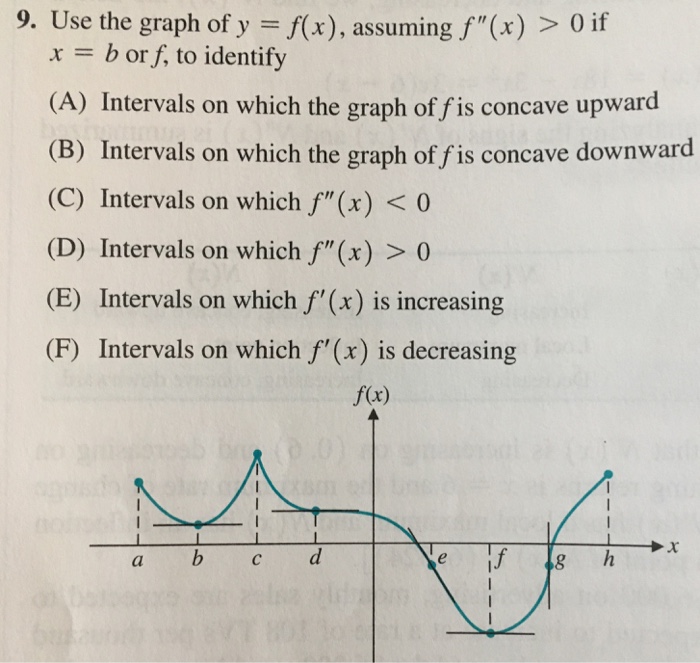



9 Use The Graph Of Y F X Assuming F X 0 If Chegg Com




Use The Given Graph Of F X To Determine The Intervals Where F X 0 F X 0 And The X Values Where F X 0 And Where F X Is Undefined Then Sketch A Graph
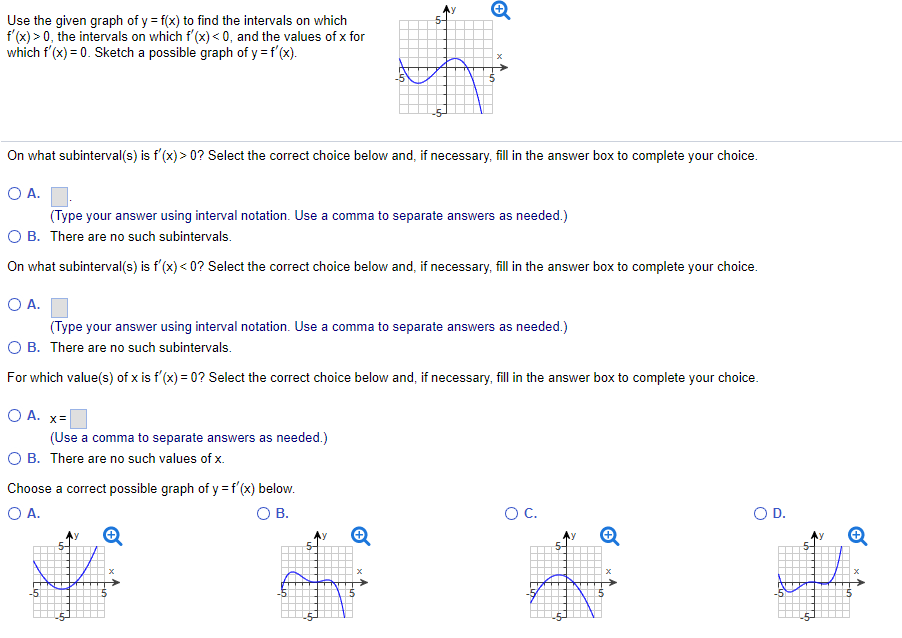



Use The Given Graph Of Y F X To Find The Intervals Chegg Com
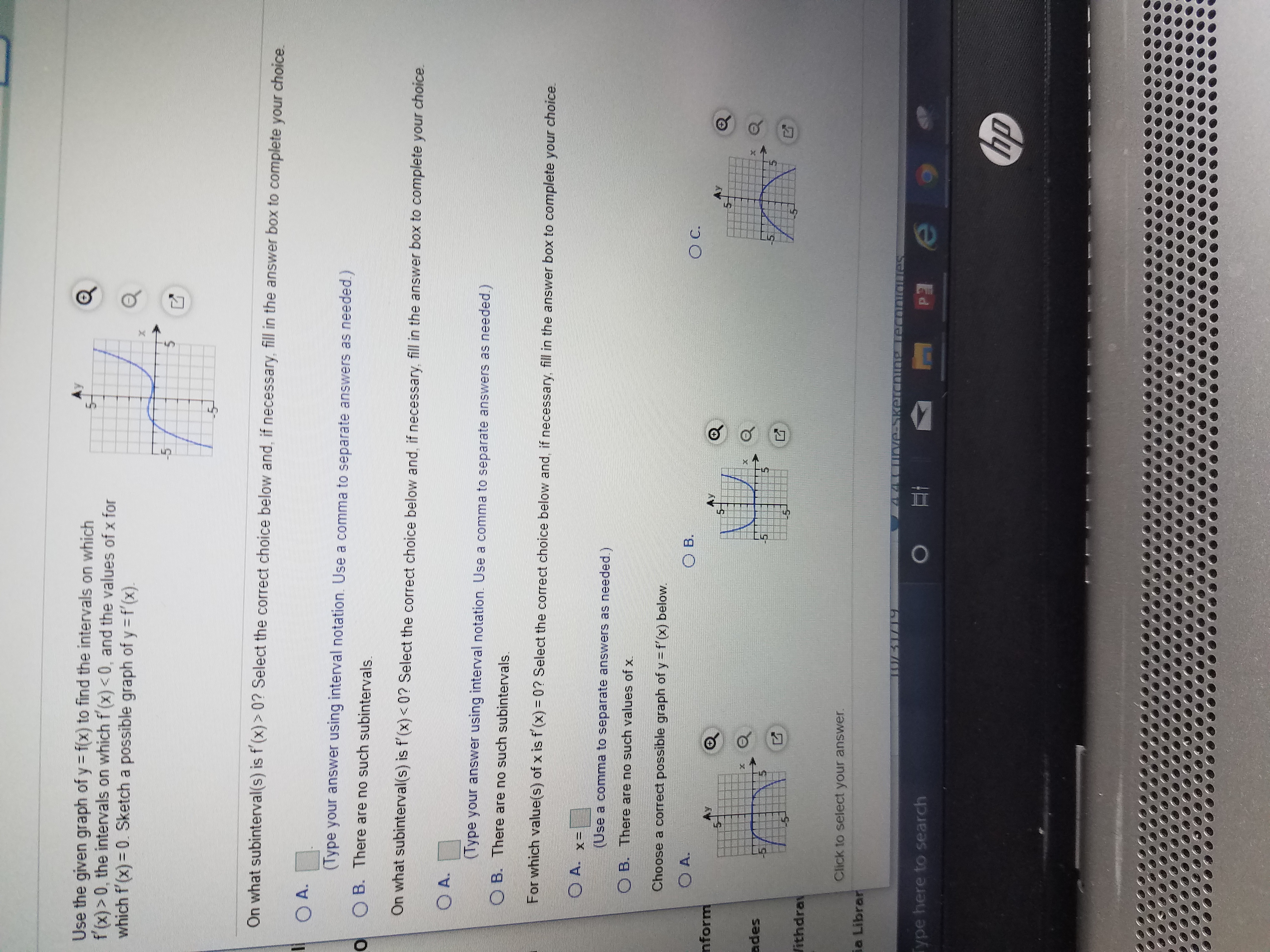



Answered Use The Given Graph Of Y F X To Find Bartleby




Which Statement Is True About The Graphed Function F X Lt 0 Over The Intervals 0 7 And Brainly Com




Select The Interval Where F X Gt 0 Brainly Com




Predict Which Statements Are True About The Intervals Of The Continuous Function Check All That Brainly Com



Yahoo Answers 04 09 Geogebra




A F X Lt 0 On The Interval X Lt 0 B F X Gt 0 On The Interval X Lt 0 C F X Lt 0 Brainly Com



Www Uplifteducation Org Cms Lib Tx Centricity Domain 273 Chapter 4 prob Pdf
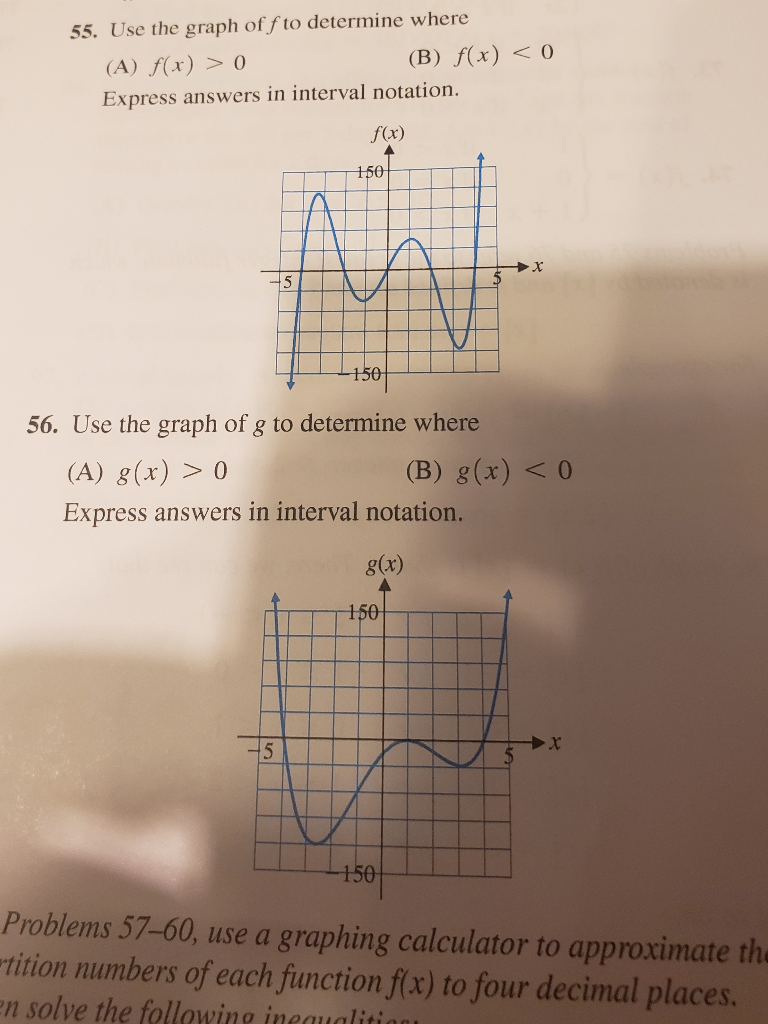



55 Use The Graph Of F To Determine Where A F X Chegg Com



How To Tell Where F X Is Less Than 0 Or Greater Than 0 Youtube




Find The Intervals In Which The Function F Given By F X 2x 2 3x Is A Strictly Increasing Youtube



4 6 1 Polynomial And Rational Inequalities Part I



Http Www Math Tamu Edu Mayaj Chapter5 Sec5p1completed Pdf



Find The Intervals Where F X 0 Ir F X 0 As Chegg Com




Piecewise Monotone Intervals Of F X X P Sin X 0 X 2p Download Scientific Diagram




Which Statement Is True About The Given Function A F X Lt 0 Over The Intervals Infinity 2 7 Brainly Com




Use The Graph Of F To Determine Where A F X 0 And Chegg Com



Function Intervals Of Increasing Or Decreasing Algebra House
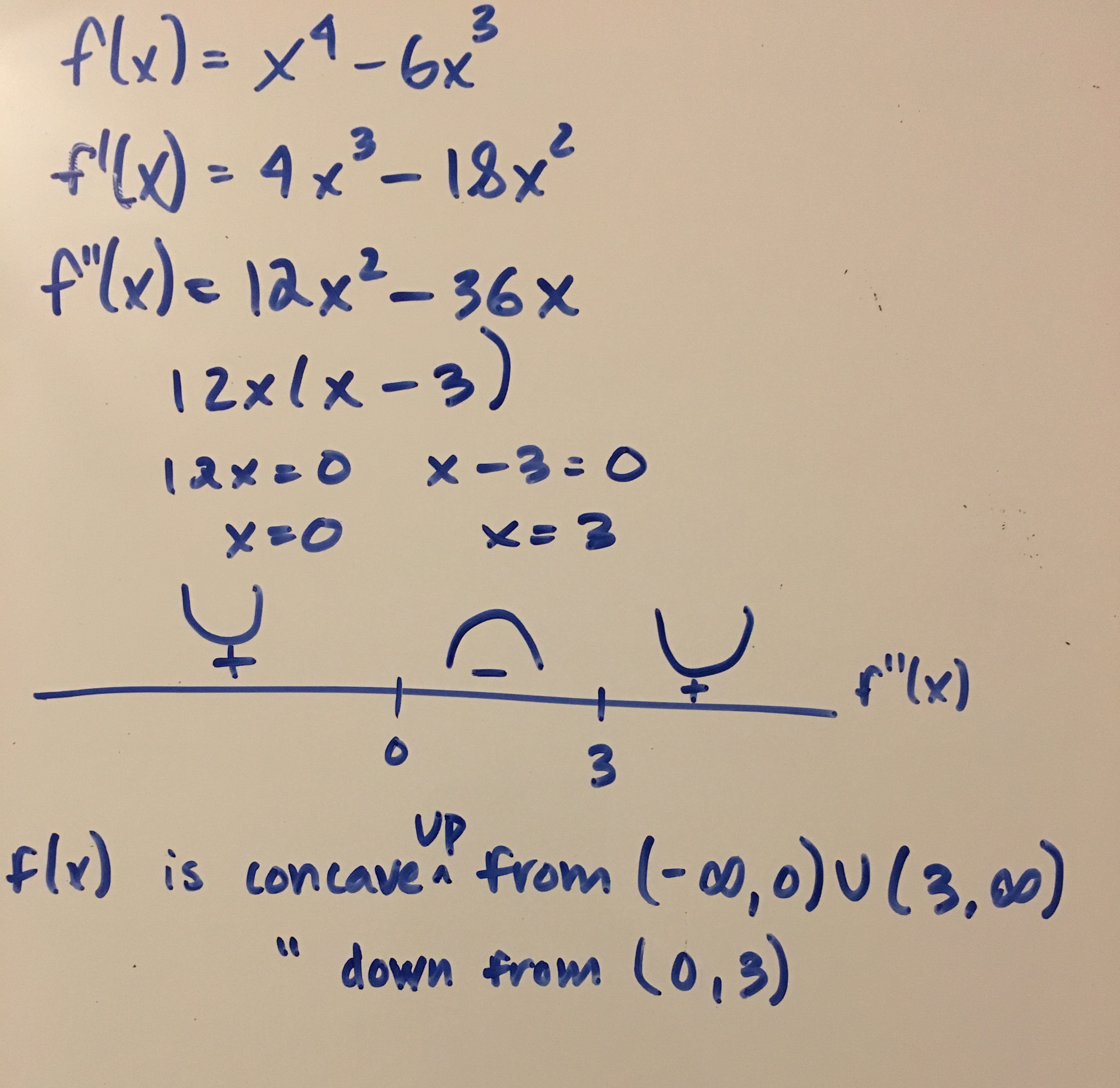



How Do You Ise Interval Notation Indicate Where F X Is Concave Up And Concave Down For F X X 4 6x 3 Socratic
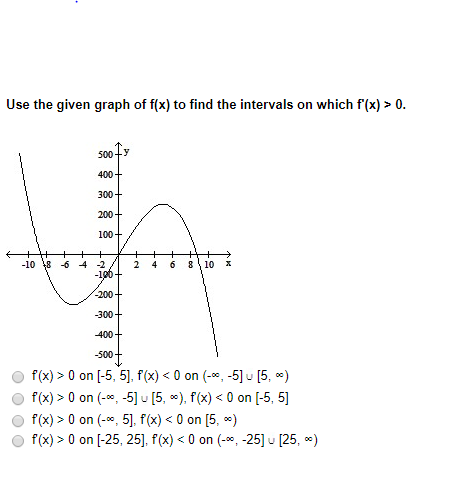



Use The Given Graph Of F X To Find The Intervals On Chegg Com



Preview 5 1 Abcdef Pg Query



Secure Media Collegeboard Org Digitalservices Pdf Ap Ap17 Calculus Q3 Pdf
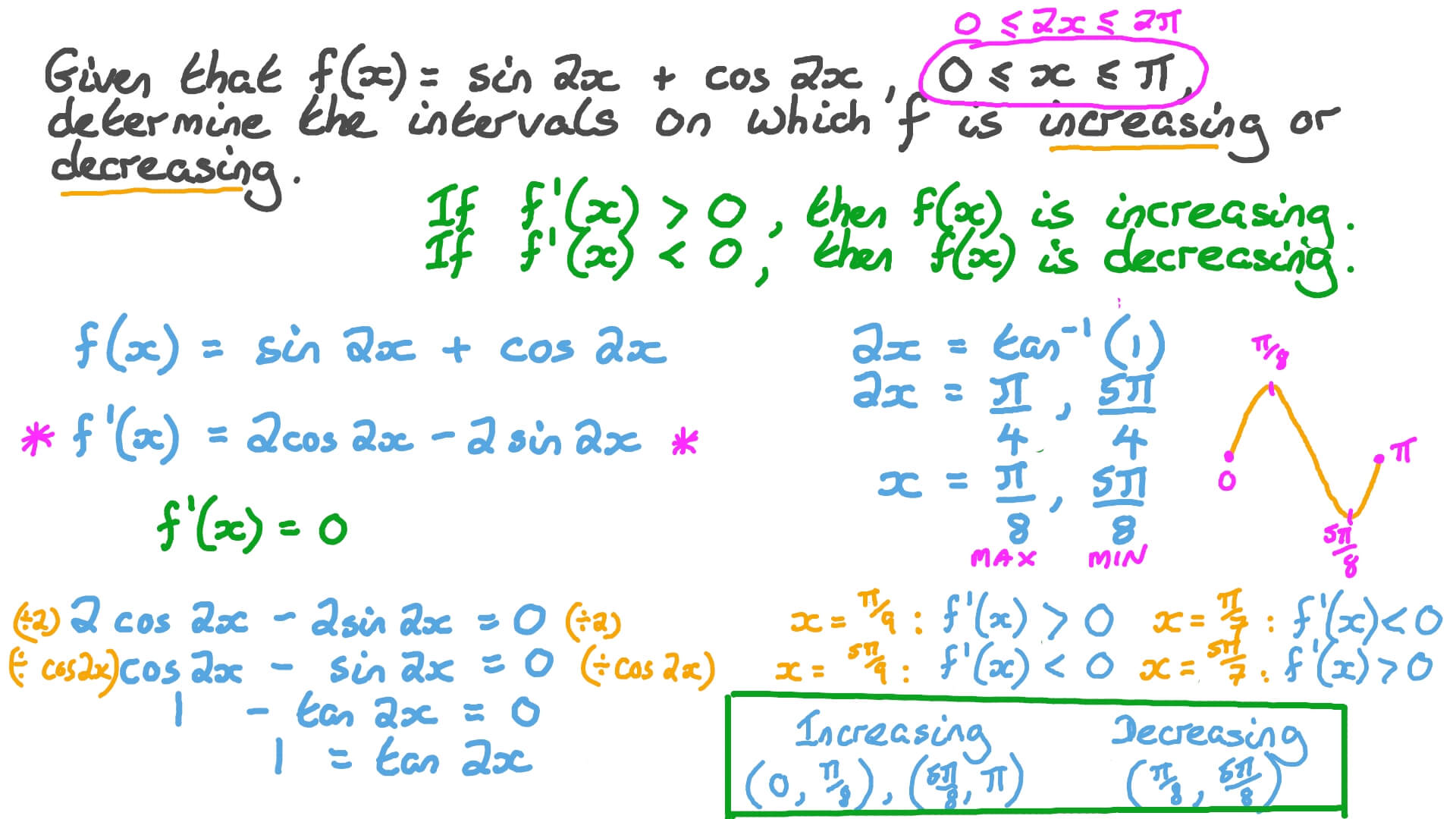



Question Video Finding The Intervals Of Increasing And Decreasing Of A Function Involving Trigonometric Functions Nagwa
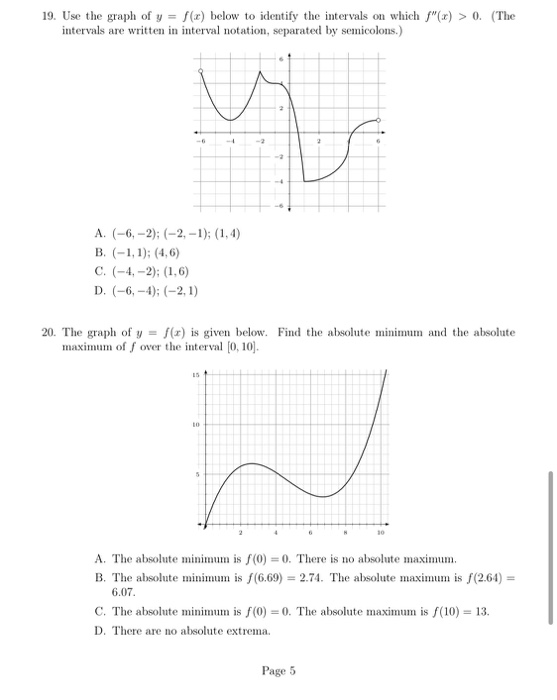



19 Use The Graph Of Y F X Below To Identify The Chegg Com
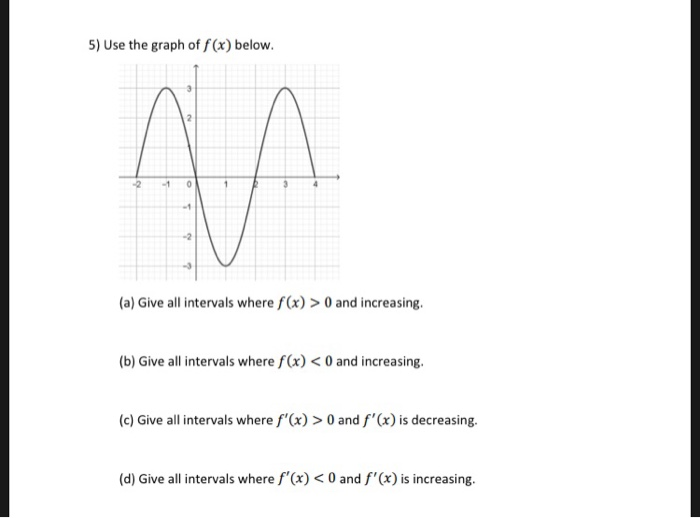



5 Use The Graph Of F X Below 1 0 2 A Give All Chegg Com



Solved Use The Given Graph Of Y F X To Find The Intervals On Which 5 7 F X Gt 0 The Intervals On Which F X Lt 0 And The Values Of X Fo
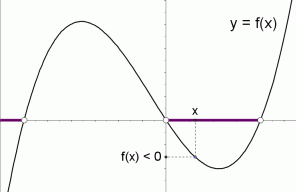



Graphical Interpretation Of Sentences Like F X 0 And F X 0




Interval Of F X Question Find The Intervals On Which F X 3x 4 4x 3 12x 2 2 Is My Working Out And Answer Correct Askmath




Use The Graph Of Y F X To Find The Intervals Of Which F X 0 The Intervals On Which F X 0 And The Values Of X For Which F X 0 Sketch A Possible Graph Of Y F X



Http Www Hershey K12 Pa Us Cms Lib Pa Centricity Domain 528 Chapter 4 review rev key Pdf
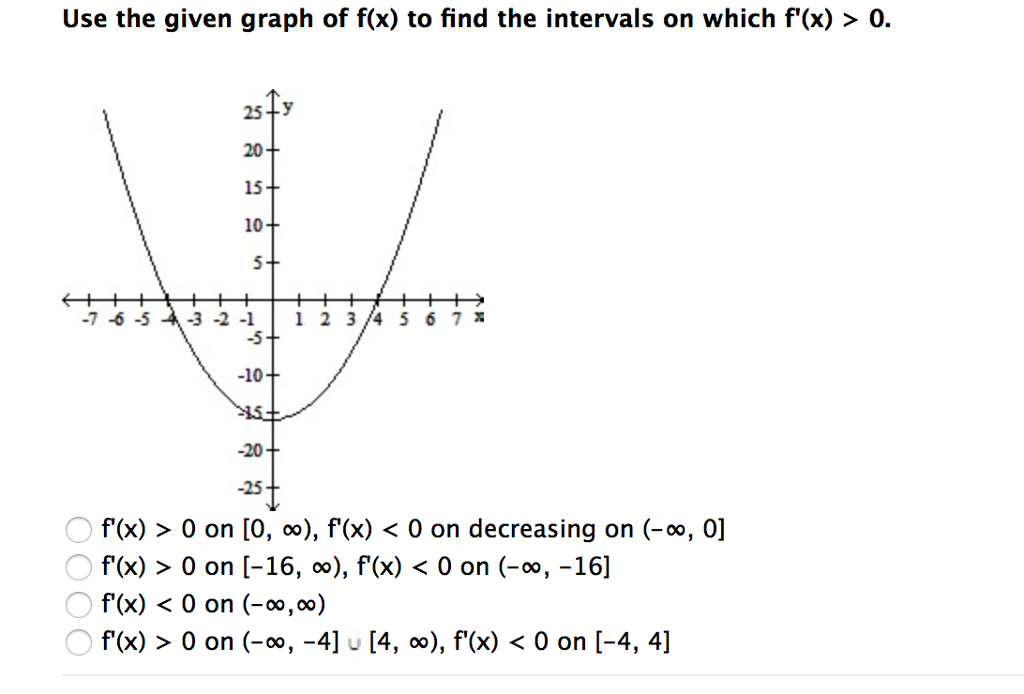



Use The Given Graph Of F X To Find The Intervals On Chegg Com
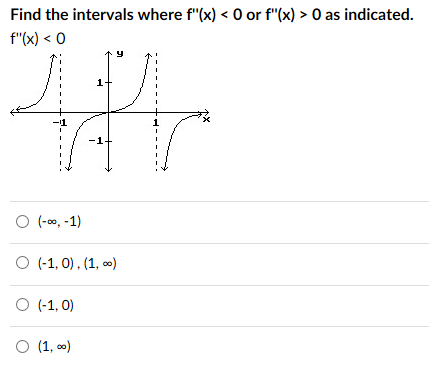



Find The Intervals Where F X 0 Or F X 0 As Chegg Com
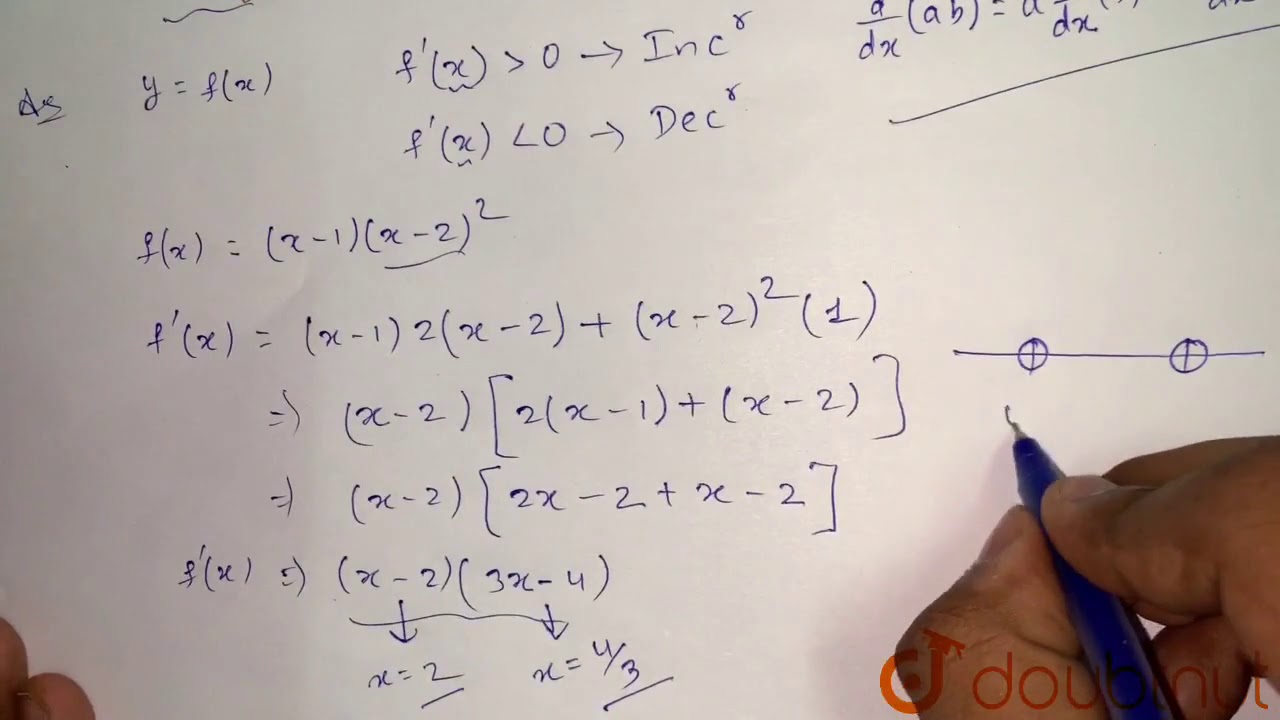



Find The Intervals In Which F X X 1 X 2 2 Is Increasing Or Decreasing Youtube



How To Find Increasing Intervals By Graphing Functions Calculus 1




Which Statement Is True About The Graphed Function F X Lt 0 Over The Intervals 0 7 And Brainly In



3
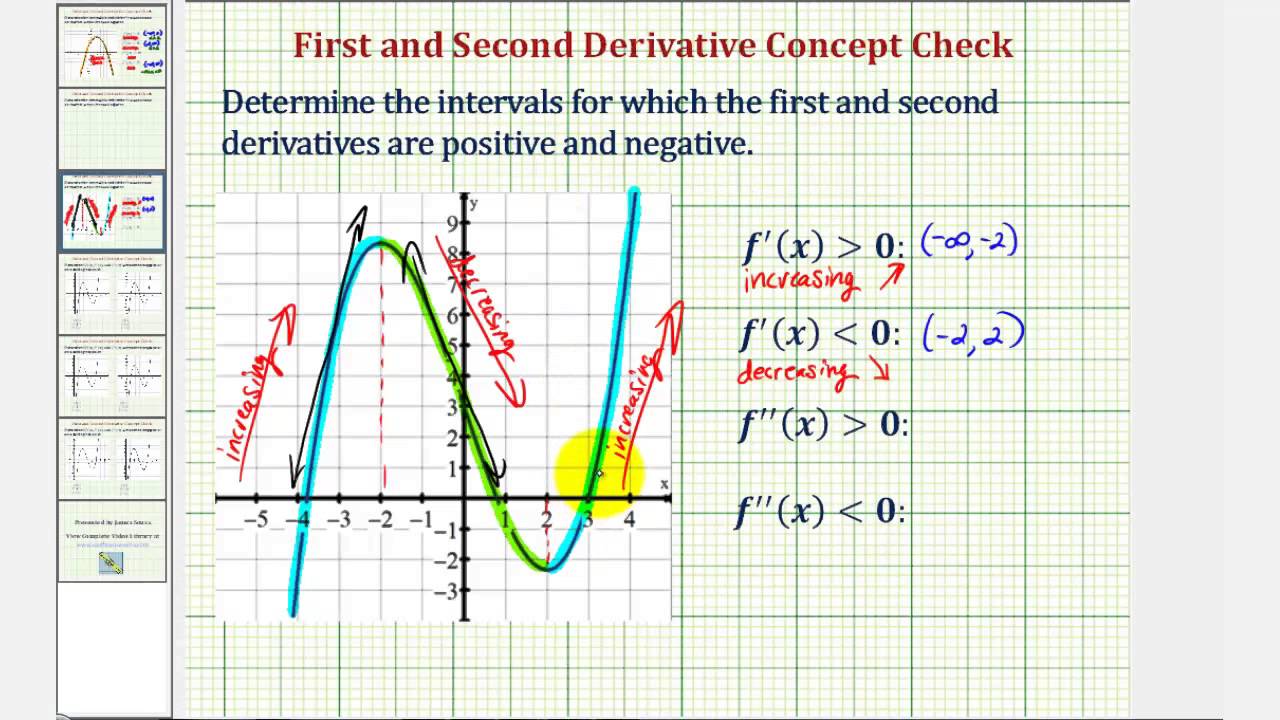



Ex 2 Intervals For Which The First And Second Derivative Are Positive And Negative Given A Graph Youtube
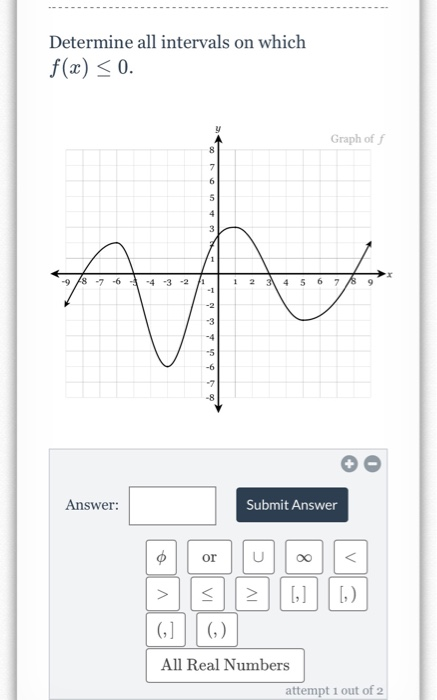



Determine All Intervals On Which F X 0 Graph Of 1 Chegg Com



How Do You Determine Whether The Function F X Ln X 2 7 Is Concave Up Or Concave Down And Its Intervals Socratic




How To Use Graph To Determine Where F X 0 And F X 0 Mathematics Stack Exchange




Answered 3 3 Increasing And Decreasing Functions Bartleby




List The Intervals On Which The Function Is Increasing By Finding Where F Grater Than 0 F X Sin 2x On 0 2pi Study Com




Answered 8 X 0 6 2 4 2 36 U Y F X 0 8 X 2 Bartleby



Search Q Point Of Inflection Tbm Isch
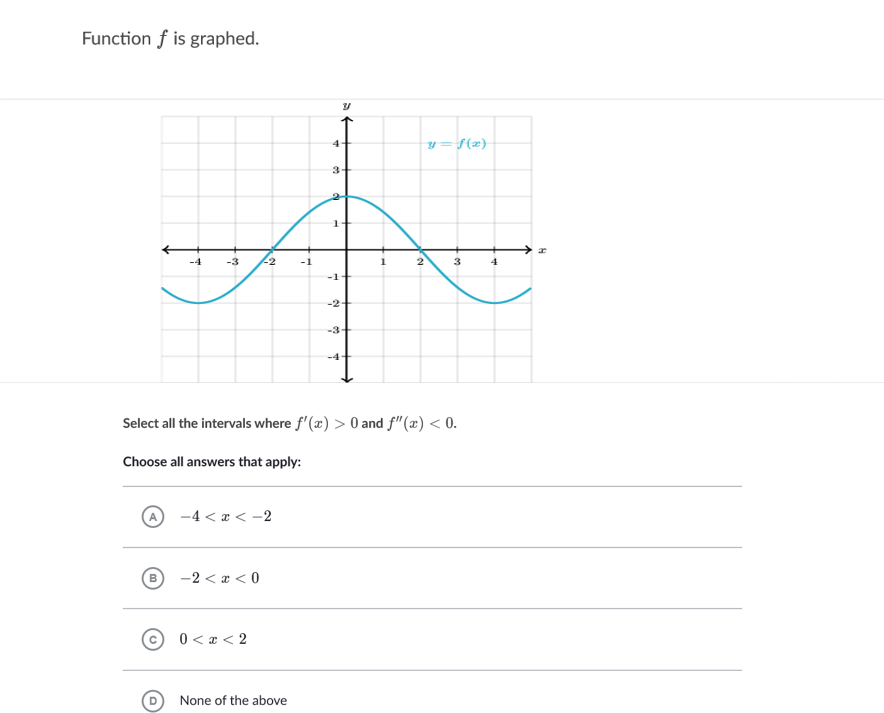



Function F Is Graphed Y F E 4 3 2 1 Select All Chegg Com



Find The Intervals In Which The Function F Given By F X Sinx Cosx 0 X 2pi Is Strictly Increasing Or Strictly Decreasing
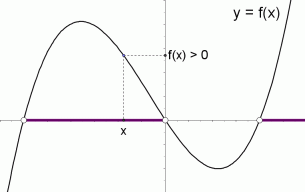



Graphical Interpretation Of Sentences Like F X 0 And F X 0



F Vs F
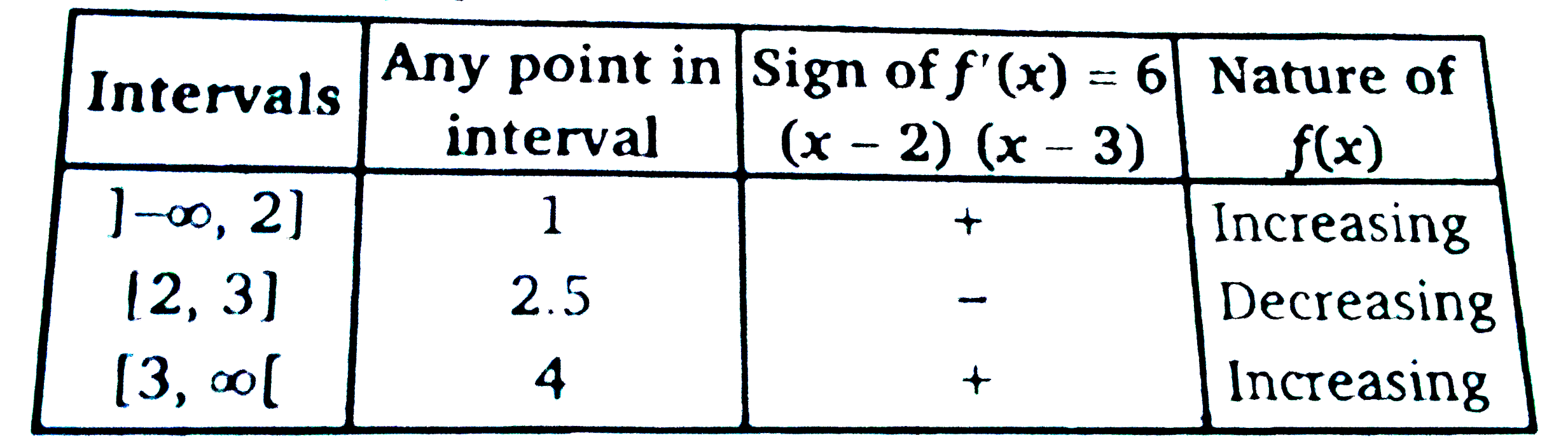



Find The Intervals In Which The Function F X 2x 3 15x 2
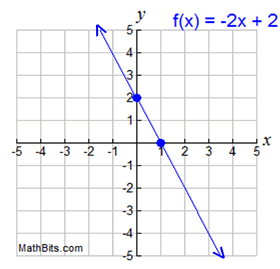



Features Of Function Graphs Mathbitsnotebook A1 Ccss Math
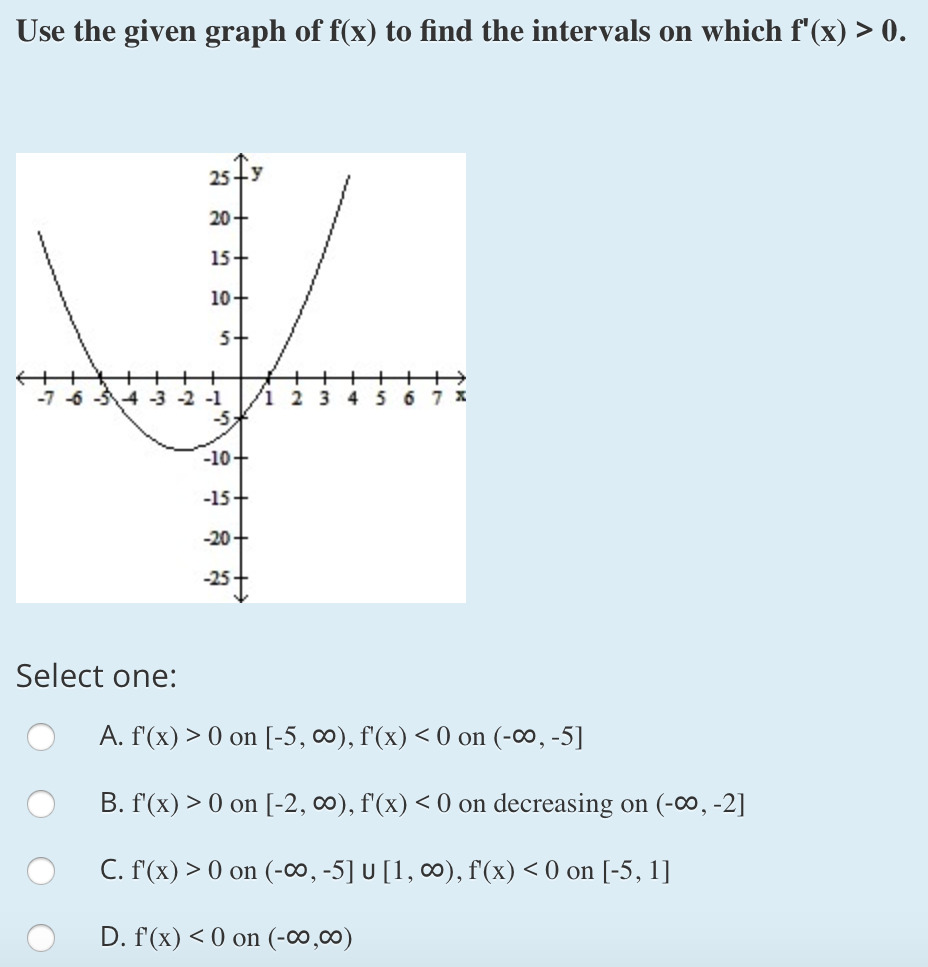



Solved Use The Given Graph Of F X To Find The Intervals Chegg Com



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿